PVC is the world’s third most widely produced synthetic plastic polymer after polyethylene and polypropylene. More than 40 million tonnes of PVC are produced each year. PVC boards are versatile construction material; it is used across different fields including the construction industry. However, in this blog post, we will try to analyze whether PVC board is worth the investment or not.
Additionally, we will contrast PVC with several PVC substitutes, including wood, WPC, MDF, and others.
What is a PVC Board?
Short for Poly Vinyl Chloride, PVC is a synthetic polymer. PVC has a honey-comb like micro-cell structure at a molecular level. It is a lightweight and durable material.
PVC boards are widely used in the construction industry. Due to their waterproofing properties, PVC boards can be used in damp environments such as Washbasin sets, kitchen cabinetry, flooring, mirror frames, and so on.
In addition to their application in the construction industry, they are also employed across different fields such as the clothing industry, manufacturing industry, electronic industry, pharmaceutical industry, packaging industry, advertising industry, and so on.
How is PVC Produced?
PVC is produced by the polymerization of vinyl chloride monomer. The three major techniques used to produce PVC are bulk, emulsion, and suspension techniques.
The raw material (Polyvinyl Monomer), which is used to make PVC, is compressed and liquefied before being added to the polymerization reactor, which also contains water and suspending agents. The initiator is then pumped into the reactor, where PVC is created at 40 to 60 degrees Celsius under a few bars.
PVC produces microscopic particles that expand until they reach the correct size, at which point the process is terminated. When PVC is finally cured, a white powder known as PVC resin results. Using this PVC resin, PVC boards are manufactured in desired shapes and sizes.
A Brief History of PVC Boards
Did you know that PVC was discovered by accident in the 18th century? Scientists observed that Vinyl chloride gas transformed when subjected to sunlight. This transformation was termed polymerization.
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) was first discovered by the German Chemist Eugen Baumann in 1872. However, the discovery wasn’t regarded as significant, therefore, he never applied for a patent.
In 1913, Friedrich Klatte invented a new method of polymerization using acetylene and hydrogen chloride, and mercuric chloride as a catalyst. For this invention, Friedrich Klatte became the first person to receive a patent for PVC.
But, until 1926 PVC had no useful application. The material became commercially useful with the invention of plasticized polyvinyl chloride by Waldo Lonsbury Semon. After this, the practical application of PVC mushroomed replacing different previously used construction materials such as metal, wood, glass, etc.
You May Also Read: 13 Cheap Concrete Alternatives – Save Money and the Planet
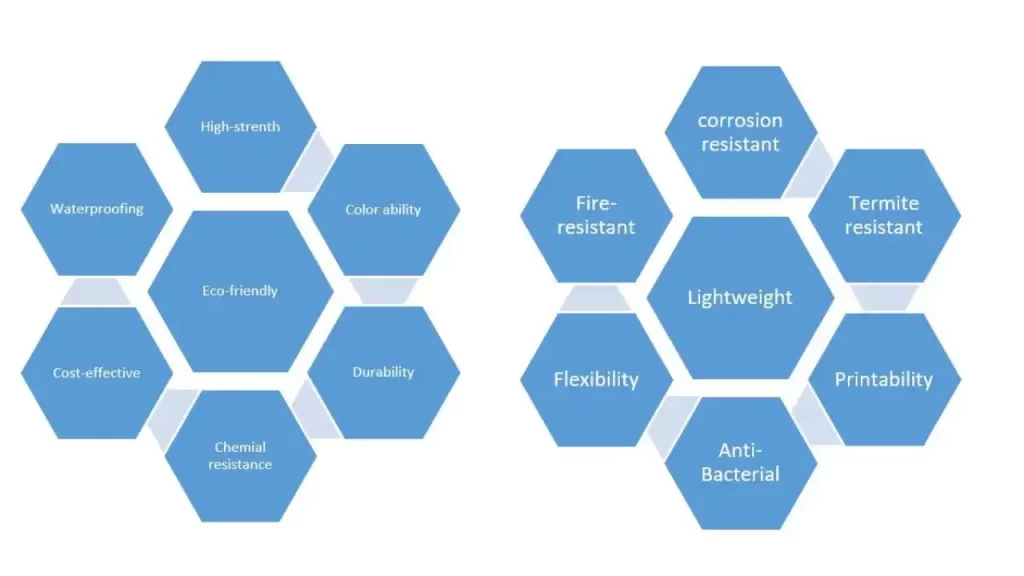
Major Properties and Advantages of PVC Boards
PVC boards are engineered to deliver excellent performance under different working conditions for a long time. PVC products can offer service for as long as 35-40 years.
Some major properties and advantages that give PVC an edge over other construction materials are shown in the figure below.
Disadvantages of PVC Boards
Although PVC boards offer a wide range of benefits, there are some downsides to using PVC boards. Some of the major drawbacks of PVC include:
- It is produced from petroleum and chlorine
- When it burns, toxic gas is released (however, during their lifespans they don’t emit any gas)
- Can get chalky and brittle if exposed to UV or Ozone
- It reacts with some solvents
- Glued joints are not so sturdy
- Thermal expansion
Types of PVC Boards
There are two major types of PVC boards, namely foam boards and hollow boards.
Hollow boards as the name implies are hollow from the inside. They are economical, light in weight, less durable, and less reliable.
While PVC foam boards are rigid and thicker, making them durable, sturdier, fire-resistant, and more reliable.
Applications of PVC Boards
We have already discussed some of the applications of PVC boards. Let’s highlight more applications of PVC boards, emphasizing commercial applications.
PVC boards are employed for both interior and exterior applications. However, the exterior application is not very widespread. For interior applications, PVC is used to manufacture furniture, cupboards, floorings, ceilings, cabinets, Washbasin sets closets, mirror frames, etc.
How is PVC Installed?
The best thing about PVC boards is the ease of installation. Usually, PVC board comes in a pre-laminated and ready-to-fit design, which requires no additional finishing. With the help of a few tools, one can install PVC boards.
When it comes to making unique and complex structures and furniture using PVC sheets. The best way is to consult an experienced carpenter or a skilled installer. Usually, the PVC boards are cut into required sizes. Then they are placed and using mechanical screws like stainless steel nails or screws, they are fastened in place.
Furthermore, to secure joints glue is used. A combination of glue and mechanical screws is the best way to keep the boards secure.
The length of the PVC board is affected slightly by temperature, therefore, it is recommended to leave some space between two adjacent boards. A length of 1/8th of an inch is recommended.
Once the installation is completed, PVC can be painted to get the desired look. It is important to understand that dark colors absorb more heat, which is not desirable. We recommend you use a lighter color with a light reflective value of 55 or more.
You May Also Read: RFID Technologies: A Game-Changer for the AEC Industry
PVC in Comparison with Other Construction Material
Now that we have a clear understanding of PVC as a construction material. We have discussed its advantages and disadvantages. Let’s compare PVC board with major construction materials, starting with the most common construction material wood.
PVC vs Wood: Which One is Better?

Wood has been used as a construction material for thousands of years. It is one of the oldest construction materials.
Wood has excellent thermal insulation properties. Additionally, it is resilient, sustainable, biodegradable, and aesthetically pleasing. Due to these qualities, wood has long been a popular building material for buildings such as homes, shelters, boats, furniture, cabinets, floors, and ceilings.
You May Also Read: BIM technologies revolutionizing the AEC industry
However, there are a few problems associated with the use of wood as a construction material, most notably:
- The use of wood sponsors deforestation
- Global attempt to preserve world food forest
- Forests help mitigate climate change
- Wood is not available everywhere
- Wood is expensive in many places around the world
- Vulnerability to termite/insect attacks
- Susceptible to fire
- Heavy
The following table shows the different properties of wood as a construction material in comparison with PVC.
| Parameter | PVC | Wood |
| Durability | More durable | Less durable than PVC |
| Flexibility | More flexible | Not Flexible |
| Maintenance | Maintenance-free | Require high maintenance |
| Termite resistance | Superior termite resistance | Susceptible to termite attack |
| Moisture resistance | Higher resistance (Water absorption rate less than 0.5%) | Absorbs moisture quickly and swells |
| Rotting | Doesn’t rot | Rot and get moldy, subsequently decays |
| Fire resistant | Highly resistant to fire | Catch fire easily |
| Eco-friendliness | More eco friendly | Leads to deforestation |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavy |
| Color option | Fewer color options available than wood | More color options are available |
| Installation | Ease of installation | Complex installation process |
| Cost Comparison | Cost-effective | expensive |
PVC Boards are increasingly replacing wood nowadays. They are cheaper, easy to install, durable, and offer better termite, moisture, and fire resistance.
But why bother looking for another material if you have access to natural wood and the cost is not a problem?
PVC vs Plywood: Which One is Better?

Plywood is an engineered timber produced by gluing multiple sheets of wood veneer through the process known as cross-graining, in which each adjacent layer of veneer is placed in such a way that wood grains are perpendicular to each other. This assembly gives strength to plywood.
In producing plywood, veneer layers are subjected to a tremendous amount of pressure of [1.9 MPa or 280 psi] and then heated up to 140 °C (284 °F).
Plywood possesses different features, such as durability, flexibility, impact tolerance, and stability. In addition, plywood has an amazing level of flame, moisture, chemical, and temperature resistance.
Therefore, due to its superior performance compared to traditional wood, Plywood has been used to produce different equipment such as cupboards, furniture, bookshelves, closets, etc.
A detailed comparison between the PVC and Plywood is presented below.
| Parameter | PVC | Plywood |
| Durability | More durable | Less durable than PVC |
| Flexibility | More flexible | Have less flexibility than PVC |
| Invented by | Henri Victor Regnault and Eugen Baumann | Immanuel Nobel |
| Raw material used | Salt and oil | Softwood, hardwood, or their combination |
| Moisture resistance | Higher resistance | Less resistant compared to PVC |
| Eco-friendliness | More eco friendly | Less eco friendly |
| Color option | Fewer color options available than Plywood | More color options are available |
Compared to PVC, plywood is more prone to termites and insect attack. However, plywood is available in more designs and color combinations.
When it comes to choosing between the two materials, it all depends upon your requirements. If you need aesthetical appeal and flexibility with the design, then you should go with plywood. If you prefer flexibility, eco-friendliness, and cost-efficiency, then PVC is the clear winner.
PVC vs MDF: Which One is Better?

MDF stands for Medium-density Fiberboard. MDF is a composite construction material produced from plantation wood. The raw material is converted into pulp and then it is re-formed into a hard product, commonly known as MDF.
MDF is a substitute for natural wood since it enhances different properties of natural wood including strength, durability, and weather resistance.
The emission of Benzene and Formaldehyde, which are dangerous to both individuals and the environment, is the main problem with the usage of MDF. The primary justification for switching from MDF to PVC boards is the discharge of these harmful pollutants.
| Parameter | PVC | MDF |
| Durability | Less durable | More durable |
| Molding | Harder to mold | easier to mold |
| Discovered | 1872 | 1960s |
| Resistance to chipping and ripping | Lower than MDF | Higher than PVC |
| Paint-ability | Harder to paint than MDF | Easier to paint |
| Density | Lower | higher |
| Cost | Cost-effective | Costly |
MDF is designed to manufacture high-end furniture, shelving, stacking, cabinets, and other related items. To be used for a wide range of applications, MDF panels are available in different thicknesses, sizes, and shapes.
While, PVC boards are used to make lower-end furniture, floor underlayment, cabinet, and other applications.
PVC vs WPC: Which One is Better?

WPC stands for Wood-Plastic Composite. WPC is composed of natural wood fiber, sawdust, plastic fiber, and chemical additives. WPC boards a usually used as a wood substitute to make cupboards, kitchen cabinets, and bathrooms.
WPC and PVC have interchangeable applications. A comparison of these two materials is shown below.
| Parameter | PVC | WPC |
| Durability | Less durable | More strength than PVC |
| Moisture resistance | Comparatively lesser | high |
| Eco-friendliness | Less eco-friendly | More eco-friendly as they are produced from recycled material and can also be reused |
| Color option | Fewer color varieties | More color varieties |
| Versatility | Less versatile | More versatility in terms of density |
| Cost | Cost-effective | Expensive |
The properties and applications of WPC and PVC boards are almost identical. However, PVC is budget-friendly as compared to WPC boards. While the performance of WPC is relatively higher since it’s expensive in comparison with PVC.
If you are intending to build a cupboard for the short term and on a small budget, then the use of PVC board is the way to go.
PVC vs Metal: Which One is Better?

The next material that can be used as an alternative to PVC boards is metal. Metal sheets are durable, strong, and lightweight construction materials that can be used for various purposes.
Metal panels come in a wide range of thicknesses, colors, designs, and finishes. Therefore, metal sheets are engineered to deliver style, utility, and quality.
Homeowners and construction professionals face confusion when deciding between metal sheets and PVC sheets. To help them make an informed decision, these two materials are compared in the table given below.
| Parameter | PVC | Metal sheets |
| Durability | Less durable | More strength than PVC |
| Moisture resistance | Comparatively lesser than metal sheets | high |
| Eco-friendliness | Less eco-friendly | More eco-friendly as they are produced from recycled material and can also be reused |
| Ease of installation | Easy | Easy |
| Additional reinforcement | Needed | Not needed |
| Cost | Cost-effective | Expensive |
| Soundproofing | Better soundproofing | Poor soundproofing |
| Dent resistance | Superior dent resistance | Poor dent resistance |
| Lifespan | Shorter | longer |
| Corrosion resistance | Better corrosion resistance | Prone to corrosion |
The choice of material depends on the purpose of the application. For instance, metal sheets are preferred for walls and ceilings of garages, while PVC is ideal for kitchen cabinets, furniture, cupboards, and other related applications.
PVC vs Aluminum: Which One is Better?

Aluminum is a durable construction material that is widely used as a wood alternative especially to make windows and doors. Aluminum is often compared with other construction materials. Let’s contrast aluminum with PVC and discuss which one is the better solution.
Although these two materials have quite diverse applications, there is nevertheless a point of contact, like as in the framing of windows and doors. A comparison of the two materials is presented in the following table.
| Parameter | PVC | Aluminum |
| Durability | Less durable | More durable |
| Moisture resistance | Less resistant than Aluminum | Zero influence of moisture |
| Cost Comparison | Cheaper | Expensive |
| Sizes | Lesser size varieties than Aluminum | Available in all sizes |
| Eco-friendliness | Less eco friendly | More eco-friendly, since it can be easily recycled and reuse |
| Weight | Heavier than Aluminum | Lightweight |
| Thermal insulation | Better thermal insulation | Lower thermal insulation than PVC |
| Resistance to environmental conditions | Less resistive | Highly resistant |
| Lifetime | Shorter | Longer |
| Corrosion resistance | Less resistance | High resistance |
| Aesthetical appeal | Inferior aesthetics than aluminum | Superior aesthetical appeal |
When making the final decision about the choice of material. It is important to keep in mind your preferences and requirements.
If you are running on a limited budget then PVC is the way to go, while if strength, durability, and glazing are the primary provisions, then it’s worth choosing aluminum.
PVC vs Glass: Which One is Better?

Glass is one of the most versatile and oldest construction materials. Due to its transparency properties, glass is an ideal option for windows, partitions, doors, and other related applications.
Can glass be substituted with another material such as PVC? Before, answering this question, let’s compare their properties.
| Parameter | PVC | Glass |
| Durability | More durable | Less durable than PVC |
| Strength | Stronger than glass | Very fragile/ Brittle |
| Transparency | Zero transparency | Highly transparent |
| Moisture resistance | Less resistance than glass | High resistance |
| Moisture resistance | Susceptible to moisture | More resistant compared to PVC |
| Eco-friendliness | Less eco-friendly than glass | More eco-friendly, since it can be easily recycled and reuse |
| Aesthetically appeal | Less versatility | Excellent aesthetical appeal |
| Flexibility | More flexibility | Easily moldable during production but possesses less flexibility after its production |
| Sustainability | Less sustainable | Highly sustainable |
| Cost | Cost-effective | Expensive than PVC |
| Impact resistance | More impact resistance than Glass | Less impact resistance |
| Thermal insulation | More thermal insulation than glass | Low thermal insulation |
Likewise, requirements and preferences dictate the choice of material. For applications where strength, energy efficiency, and cost are the primary requirements, then PVC is the better solution.
While for other uses, where transparency, aesthetical appeal, and sustainability are needed, then the glass is a better option than PVC.
Is PVC the Best Construction Material?
Let’s hold off on making assumptions. The purpose, preferences, needs, weather, location, and other considerations are just a few that come into play while choosing a building material.
PVC could be the ideal material for one application but not the best choice for another. So, is PVC a wise investment? The short answer is Yes. PVC delivers strength, quality, aesthetic appeal, and a wide range of application options. PVC provides value for the investment as a result.
Closing Remarks
PVC is an economical and sturdy option when it comes to building interior designs. If you are looking for a high-quality, durable and attractive construction material, PVC is an incredible option. Feel free to reach out to us if you have any questions.
