RFID Technologies are employed across different fields, likewise, the construction industry is also adopting the technology. However, construction professionals are hesitant toward the full implementation of this technology.
In this blog post, we will try to dissect the concept and will discuss how RFID technologies can transform the AEC industry.
Concept of a Smart Environment
The idea of a smart environment is proposed by Philips in 1999.
A smart environment is an assembly where different technological devices such as sensors, appliances, embedded systems, actuators, computers, readers, etc., work continuously to provide services for the betterment of human life.
The gadgets used are invisible and intrusive to the users thus making them easy to work and interact with. Moreover, the use of such technology improves efficiency and user experience.
You May Also Read: 13 Cheap Concrete Alternatives – Save Money and the Planet
In a smart environment, manual, repetitive, risky, and labor extensive processes are replaced with automation that is less demanding of the users such as remote control, image processing, wireless communication, speech recognition, computer networking, touch-sensitive screens, wireless sensors, and so on.
Likewise, Radio-frequency identification is an essential element in building a smart environment.
What is Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID)?
Radio-frequency Identification or RFID is an automatic tracking system that uses electromagnetic signals to acquire information about different objectives and parameters. A typical RFID system comprises tags, readers/scanners, and a data processing system.
An RFID tag is programmed to record, receive and forward Electronic Product Codes (EPC). Digital data is encoded into smart tags or labels which are captured by radio wave readers or scanners.
According to the report by Research Dive, the global RFID market is projected to garner $21.361 Billion by 2027. The industry is expected to grow at 9.9% CAGR during the timeframe (2020-2027).
You May Also Read: BIM technologies revolutionizing the AEC industry
History of RFID Technologies
The history of RFID technology can be traced back to World War 2 when technologies such as the Identification friend and foe transponder were used by the Allies and Germany to identify aircraft as friendly or hostile.
However, Mario Cardullo’s device (patented on 23rd January 1973) was the first true ancestor of modern RFID technologies. It was a passive radio transponder with 16-bit memory storage.
The device was used in the transportation industry for automotive vehicle identification, automatic toll system, vehicle routing, etc.
Steven Depp, Alfred Koelle, and Robert Frayman gave a pioneering demonstration of passive and semi-passive RFID tags with reflected power in 1973.
Charles Walton received the initial patent related to the acronym RFID in 1983.
Over time, RFID technologies were used for different purposes, including human implantation, waste management, animal identification, and so on. Applications of RFID technology are discussed in the later sections.
You May Also Read: 5 Best Drones for Solar Inspections to Buy
Barcode vs RFID Technologies
RFID technology is comparable to a barcode system in working but it is more advance and accurate. Some of the differences that distinguish an RFID system from a barcode system are as follows:
- RFID can store more data than a typical barcode system
- An RFID Scanner can capture data even if the object is out of sight
- RFID systems have faster response times
- It uses object identification capacity
- It is not susceptible to damages
- RFID systems need minimal maintenance
- An RFID scanner can read hundreds of tags simultaneously
RFID Tags
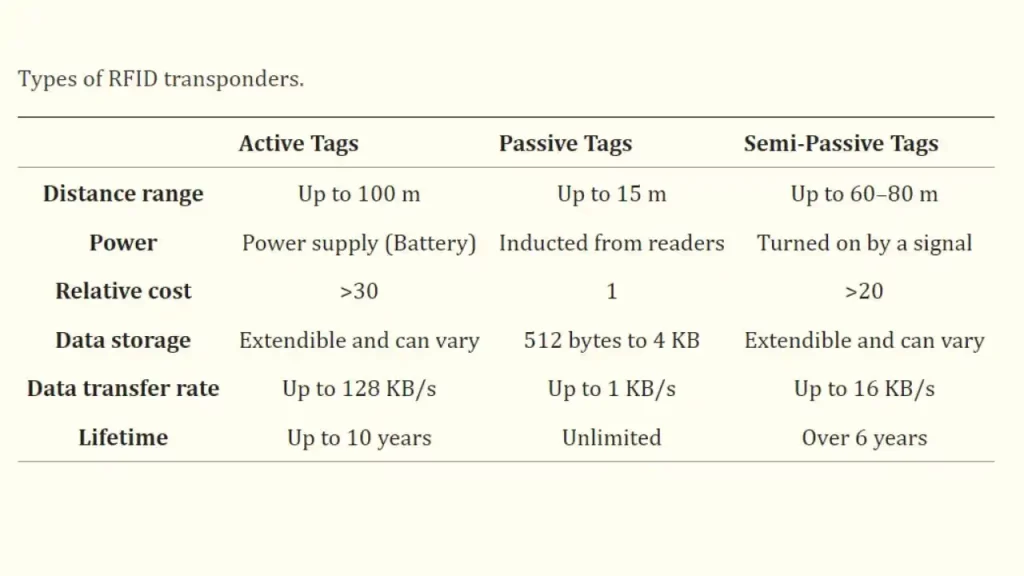
A tag or label is a critical component of an RFID system. Broadly speaking, there are three main RFID tags, namely Passive, semi-active and Active RFID tags.
- Passive RFID tag: It is a tag that doesn’t use battery power instead it gets its power from the reader. These tags are relatively cheaper and convenient for tracking within short distance ranges.
- Semi-active tag: This type of tag receives the signal from the reader but gets its energy from a peripheral battery. This type of tag has a faster response rate than passive tags.
- Active RFID tag: It is a type of RFID tag that gets its power from a battery making them suitable for long-distance data transmission. Active tags have a microchip and antenna. Active tags are generally used in high-value products or for environments that require monitoring from long distances.
RFID tags operate in different bands; a summary of the operation bands of RFID technology is shown in the table below source.
RFID Systems
Based on the type of reader and tag, RFID systems can be categorized into three groups;
- Passive Reader Active Tag (PRAT) system: It is a system of RFID technology where a passive reader receives a signal from an active tag. The reception range of this system can be adjusted from 0-600m.
- Active Reader Passive Tag (ARPT) system: It has an active reader which receives a signal from a passive tag.
- Active Reader Active Tag (ARAT) system: This system uses an active reader to receive data from an active tag.
Applications of RFID Technology
RFID Technologies are used for different applications ranging across several fields.
Major applications of RFID technologies include personnel tracking, access management, inventory management, ID badging, restricted area access monitoring, contactless payments, toll collection, supply chain management, wireless measurement, counterfeit prevention, and so on.
The application of RFID technology is not restricted to just one or two fields, rather its application can be extended to almost every industry. Some industries that have employed RFID technologies are as follow:
- Construction industry
- Commerce and financial sector
- Retail industry
- Food industry
- Advertising industry
- Pharmaceutical industry
- Health care sector
- Educational institutions
- Aerospace industry
- Defence
- Manufacturing industry
- Medical industry
- Transportation industry
RFID Technology in the Construction Industry
Several technological applications have been deployed in the construction industry. Likewise, the application of RFID technology continues to grow as the cost of RFID technology drops.
RFID technology has been employed in the construction industry for more than two decades now. RFID technology can facilitate the control of a wide range of processes throughout the lifecycle of a construction project from its conceptualization to completion and maintenance.
Construction management, supply chain management, inventory management, and personnel, equipment, and material tracking are all made possible by RFID technology. RFID is also utilized to increase worker safety and productivity in the construction industry.
You May Also Read: Top 23 Tools BIM Coordinator Need in 2024: A Career Guide
How RFID Technologies Can Transform the AEC Industry?
RFID technology has the potential to revolutionize the construction industry. RFID can benefit the construction industry in several ways, such as:
a) Better Resource Management
During construction, a team of employees with equipment and vehicles and hundreds of items are continually shifting positions. Better project outcomes may result from the regulation of these motions.
Moreover, the construction industry involves multiple stakeholders including contractors, engineers, architects, principals, and so on. It’s challenging to handle because of the intricate web of liaisons.
Thanks to RFID technology, managing resources, and the workforce is stress-free and error-free.
b) Enhances the Visibility of Objects in a Supply Chain
Different tools and equipment are used on construction sites and their constantly changing positions make it challenging to manage. They are often misplaced and often get lost on the site.
RFID applications can enhance the visibility of objects in a supply chain. Thus eliminating the chance of misplacing and getting lost.
c) Workforce Management
In addition to managing material resources, RFID technology also helps in managing human resources.
Hundreds and even thousands of workers work on a construction site. RFID-enabled solutions can keep track of every worker on the site as well as their identities. In this way, labor management is carried out effectively. In addition, it also improves labor efficiency.
d) Increases Supply Chain Efficiency
RFID technology can improve the efficiency of the supply chain of any construction project. RFID solutions can help construction professionals in tracking and managing every resource and process of any construction project.
e) Real-Time Data Exchange
Real-time data exchange via RFID solutions can help construction professionals in taking well-informed and timely decisions, which helps reduce costs, and risks, and improve productivity.
f) Enhancing Safety
Safety is the major concern of any construction project. To ensure workers’ safety different methods are used such as installing readers around potential hazards like open elevator shafts or guardrails.
When a worker wearing a tag approaches a potential hazard, an alarm is activated thus notifying them before any hazard.
Moreover, RFID technology offers fall protection. It allows tracking the location, maintenance, and inspection of the various fall protection systems on the site.
g) Reduce Cost and Material Waste
Better management of resources including human and material resources can lead to a reduction in material wastage. Through better management, the overall cost of the construction project is minimized.
You May Also Read: BIM sustainable construction: A step towards a sustainable future
How to Choose an RFID Technology For Your Firm?
There are a few important considerations you should make while selecting a dependable RFID system for your company, which are briefly mentioned here.
1. Safety
Safety is the major concern of the AEC industry. The RFID system to be deployed must be safe for both humans and animals.
2. The Purpose of Implementing the Technology
Make sure to choose the right system for the right application. If you choose the wrong system, it will not only cost you more money but also affects your productivity.
3. Cost of the System
Cost is another key constraint that reduces the implementation of any novel technology like RFID. The system should be affordable and the running cost should be minimal.
4. Ease of Use
The ease of use is another key consideration. You can’t afford to purchase a sophisticated system that is hard to operate. The system should be easy to mobilize, simple and user-friendly.
5. Ruggedness
The system should be rugged enough to withstand harsh construction environments. It should have superior resistance against moisture, dust, snow, mud, and wind.
6. Compatibility
The system should be compatible with other technologies such as laser scanning, BIM, virtual reality, etc.
Steps Involved in the Implementation of RFID Technologies
S.L. Ting, Albert H.C. Tsang, and Y.K. Tse (2013) have proposed a 6-step generic framework (shown in the figure below) for the implementation of RFID systems. This ensures a systematic and holistic implementation of the system.
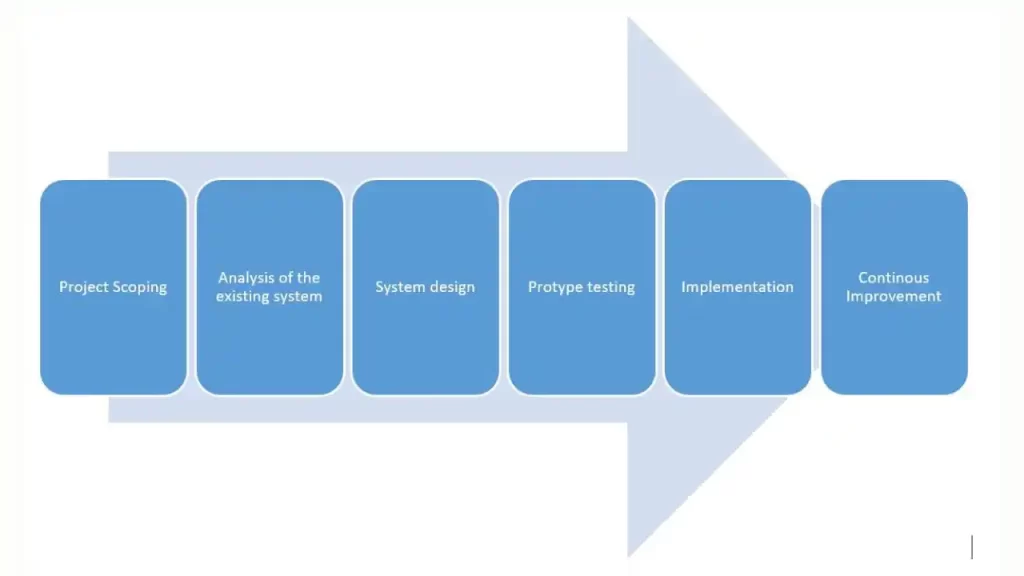
Let’s briefly discuss each step.
Step #1 Project Scoping
The first step is to identify and understand the limitations of RFID systems. Moreover, the objectives of the project where the RFID system is to be implemented are defined in the first step.
Step #2 Analysis of the Existing System
In the second step, information is collected on the existing systems using various methods such as interviews and observations. It is important to only collect information relevant to the RFID implementation process.
Followed by data collection, the analysis and evaluation of the information help identify the weaknesses and issues in the current system. Moreover, the demand for RFID technology implementation is also determined in this step.
Step #3 System Design
After the detailed analysis of the existing system, next the requirements for the new system are defined and analyzed. Keeping in mind those needs and requirements, a new system is designed.
This newly proposed system design should incorporate requirement analysis, hardware and software selection, and the development of the new process.
The hardware should be selected based on environmental factors. The material of the tagged object should be rugged enough to withstand harsh environmental conditions.
Step #4 Prototype Testing
Before the actual implementation of the system, it is essential to test a prototype to ensure that the workflow developed with RFID technology will work and the system is ready for deployment.
Once the prototype testing is complete and anticipated results are obtained. The firm should proceed with the actual implementation of the RFID technology.
Prototype testing may be conducted in a laboratory or the actual environment. However, onsite testing is a more reliable option.
The whole system including its hardware and software components is tested. Bugs and failures of systems may be detected and reported.
Step #5 Implementation
Once prototype testing is successfully conducted. The firm may proceed with the implementation of the actual system.
This step involves the installation and commissioning of hardware and software systems. It also involves change management, training, and system deployment.
During the installation, the placement of antennas and tags should be carried out with utmost care to improve efficiency and eliminate errors.
Step #6 Continuous Improvement
The last step involved in the implementation of RFID technology is continuous improvement. After system deployment, the performance of the RFID systems is monitored, employee feedback is collected, and compared with the objectives.
The project team closely monitors the system and flaws in the system are identified and addressed, thus improving the system.
RFID technology can be integrated with other technologies such as Building Information Modeling (BIM), laser scanning, PDAs, Mobile Computing, General Packet Radio Systems (GPRS), Global Positioning systems (GPS), and photogrammetry to mention a few.
Barriers to the Implementation of RFID Technologies in the Construction Industry
The global adoption of RFID technology in the construction sector is still immature. Several barriers have impeded the mass adoption of this technology, including;
1. Lack of Standards
To prevent injuries to humans and animals, Radio Frequency transmission needs to be monitored. There is a dire need for uniform global standardization. For this purpose, several organizations have set standards for RFID including the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), ASTM International, the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), etc.
Although general guidelines and standards have been devised. However, there is a lack of standards specific to the construction industry.
2. High Upfront Cost
One of the biggest obstacles to the use of RFID technology in the construction sector is cost. Despite reductions in price over the past few years, RFID systems are still somewhat pricey. As a result, building firms are reluctant to make technological investments. They are dubious about the investment’s value in RFID technology.
Governments should provide subsidies for RFID technology to make it more accessible and inexpensive, especially for small construction enterprises, in order to ensure more use in the sector.
3. Low Demand
Construction companies have not realized the potential of RFID technology, therefore, the current demand for RFID technologies is low.
5. Motivation for Adoption
The motivation of construction professionals is important for the adoption of RFID systems. However, due to a lack of vision and awareness, construction professionals are hesitant in investing.
6. Security Concerns
RFID solutions are vulnerable to hacking and unauthorized tracking, much like other systems. Readable tags increase the possibility of sensitive and private data being compromised.
Key Players in the RFID Market
The report by Research Dive lists some major players in the global RFID industry, including:
- HID Global
- Honeywell
- Nedap
- Impinj
- Zebra Technologies
- GAO RFID
- Identiv
- NXP Semiconductors,
- Avery Dennison
- Invengo
Conclusion
The construction industry cannot achieve sustainability without automating and implementing technology like RFID and BIM. Technology is the key to growth and better project outcomes. Through the application of RFID technology, sustainable construction can be ensured.